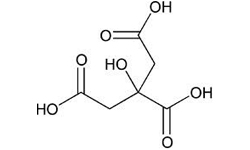
Citric Acid Anhydrous
Description
Citric Acid Anhydrous is used in confectioneries, and food products like biscuits and concentrated juices (solid form)
NSF Certified Product-NSF/ANSI 60
Applications and Effects
It is mainly used for the purpose of making the juices and also in confectioneries so that the products last longer as 90 days.
Specifications
| Tests | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Description | Colorless, translucent crystals, or white, granular to fine, crystalline powder. Melts at about 153° C with decomposition. |
| Solubility | Very soluble in water; Freely soluble in alcohol; very slightly soluble in ether. |
| Identification | By Infrared absorption. Dry the substance to be examined at 105° C for 2 hours. |
| Clarity of Solution | The test solution shows the same clarity as that of water. |
| Color of Solution | The test solution is not more intensely colored than standard solution A, B or C, or water. |
| Water | Not more than 1.0%. |
| Residue on ignition | Not more than 0.1 % determined on 1.0 g |
| Readily carbonizable substances | The color of the acid is not darker than that of a similar volume of Matching Fluid K in a matching tube, the tubes being observed vertically against a white background. |
| Sulfate | Not more than 0.015% |
| Heavy Metals | Not more than 0.001% |
| Limit of oxalic acid | Not more than 0.036% |
| Assay | 99.5% to 100.5%. (On Anhydrous basis) |
| Tests | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White or almost white, crystalline powder, colourless crystals or granules. |
| Solubility | Very soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
| Identification | First identification B, E. Second Identification A, C, D, E. |
| (A) The solution is strongly acidic. | |
| (B) By IR. Dry the substance to be examined and the reference substance at 100 – 105° C for 2 h. | |
| (C) A red colour develops. | |
| (D) A white precipitate is formed. | |
| (E) Water. | |
| Appearance of solution | The Solution is clear and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y7, BY7 or GY7. (Method II ) |
| Readily carbonisable Substances | The solution is not more intensely coloured than a mixture of 1 ml of red primary solution and 9 ml of yellow primary solution. |
| Oxalic acid | Not more than 360 ppm. |
| Sulphates | Not more than 150 ppm |
| Heavy metals | Not more than 10 ppm |
| Water | Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 2.0 g. |
| Sulphated ash | Not more than 0.1%, determined on 1.0 g |
| Assay | 99.5 % to 100.5 % , (on Anhydrous basis) |
| Tests | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Description | Colourless crystals or a white powder; slightly hygroscopic in moist dry air. |
| Solubility | Very soluble in water; Freely soluble in ethanol (95%); sparingly soluble in ether. |
| Identification (A) | (A)Determine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry. Compare the spectrum with that obtained with citric acid RS or with the reference spectrum of citric acid. Dry the substance under examination and the reference substance at 1050 for 2 hour. |
| (B) | Gives reaction A of citrates, (A) A white precipitate soluble in 6M acetic acid. |
| (C) | 10 percent w/v solution is strongly acidic. |
| Appearance of solution | The solution is clear and not more intensely coloured than reference solution YS7, BYS7 or GYS7. |
| Arsenic | Not more than 1 ppm |
| Barium | Any opalescence produced is not more intense than that of a mixture of 5 ml of solution A and 5 ml of distilled water. |
| Calcium | Not more than 200 ppm |
| Heavy metals | Not more than 10 ppm |
| Iron | Not more than 50 ppm |
| Chloride | Not more than 50 ppm |
| Sulphate | Not more than 150 ppm |
| Oxalic acid | Any pink colour produced is not more intense than that produced by carrying out the test using 0.2ml of oxalic acid dissolved in 4 ml of water. |
| Readily carbonisable Substances | Any colour produced is not more intense than that of the mixture of 1.0 ml of CCS and 9.0 ml of FCS. |
| Sulphated ash | Not more than 0.1% |
| Water | Not more than 1.0%, determined on 2.0 g. |
| Assay | 99.0 % to 101.0 % (On Anhydrous basis) |
| Tests | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Description | Colourless crystals or a white, crystalline powder; slightly efflorescent in warm, dry air. |
| Solubility | Very soluble in water; Freely soluble in ethanol (95%); sparingly soluble in ether. |
| Identification (A) | Determine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry. Compare the spectrum with that obtained with citric acid monohydrate RS or with the reference spectrum of citric acid monohydrate. Dry the substance under examination and the reference substance at 105° C for 2 hours. |
| (B) | Gives reaction A of citrates, (A) A white precipitate soluble in 6M acetic acid. |
| (C) | 10 percent w/v solution is strongly acidic. |
| Appearance of solution | The solution is clear and not more intensely coloured than reference solution YS7, BYS7 or GYS7. |
| Arsenic | Not more than 1 ppm |
| Barium | Any opalescence produced is not more intense than that of a mixture of 5 ml of solution A and 5 ml of distilled water. |
| Calcium | Not more than 200 ppm |
| Heavy metals | Not more than 10 ppm |
| Iron | Not more than 50 ppm |
| Chloride | Not more than 50 ppm |
| Sulphate | Not more than 150 ppm |
| Oxalic acid | Any pink colour produced is not more intense than that produced by carrying out the test using 0.2ml of oxalic acid dissolved in 4 ml of water. |
| Readily carbonisable Substances | Any colour produced is not more intense than that of the mixture of 1.0 ml of CCS and 9.0 ml of FCS. |
| Sulphated ash | Not more than 0.1% |
| Water | 7.5 to 9.0%, determined on 0.5 g. |
| Assay | 99.0% to 101.0% (On Anhydrous Basis) |
| Tests | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Description | Colourless crystals or a white, crystalline powder; slightly efflorescent in warm, dry air. |
| Solubility | Very soluble in water; Freely soluble in ethanol (95%); sparingly soluble in ether. |
| Identification (A) | Determine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry. Compare the spectrum with that obtained with citric acid monohydrate RS or with the reference spectrum of citric acid monohydrate. Dry the substance under examination and the reference substance at 105° C for 2 hours. |
| (B) | Gives reaction A of citrates, (A) A white precipitate soluble in 6M acetic acid. |
| (C) | 10 percent w/v solution is strongly acidic. |
| Appearance of solution | The solution is clear and not more intensely coloured than reference solution YS7, BYS7 or GYS7. |
| Arsenic | Not more than 1 ppm |
| Barium | Any opalescence produced is not more intense than that of a mixture of 5 ml of solution A and 5 ml of distilled water. |
| Calcium | Not more than 200 ppm |
| Heavy metals | Not more than 10 ppm |
| Iron | Not more than 50 ppm |
| Chloride | Not more than 50 ppm |
| Sulphate | Not more than 150 ppm |
| Oxalic acid | Any pink colour produced is not more intense than that produced by carrying out the test using 0.2ml of oxalic acid dissolved in 4 ml of water. |
| Readily carbonisable Substances | Any colour produced is not more intense than that of the mixture of 1.0 ml of CCS and 9.0 ml of FCS. |
| Sulphated ash | Not more than 0.1% |
| Water | 7.5 to 9.0%, determined on 0.5 g. |
| Assay | 99.0% to 101.0% (On Anhydrous Basis) |
