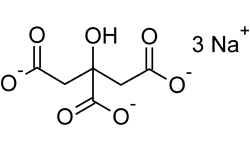
Sodium Citrate (Trisodium Citrate) Chemical Formula
Description
Sodium Citrate is mainly used as an expectorant and a urine alkanizer. It is also used as a pharmaceutical aid and as a food additive in Dairy Industries which cater in Cheese Manufacturing and Beverages. It is also a water treatment chemical and as a Laboratory Reagent.
Applications and Effects
Our product helps in the storage of all the Dairy products especially cheese. It can prevent the dairy products from getting stale for 90 days than compared to other solutions. If it is used in water then can prevent the growth of bacteria for 15 days.
Specifications
| Tests | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Description | Colorless crystals or white, crystalline powder. |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in water and very soluble in boiling water. Insoluble in alcohol. |
| Identification | A) solution (1 in 20) responds to the test for Sodium and for citrate. Sodium: A dense precipitate is formed. Citrate: A light red colour is produced. |
| Alkalinity | No pink colour is produced by 1 drop of phenolphthalein TS. |
| Water | Between 10.0% and 13.0%. Dry it at 180°C for 18 hours. |
| Alkalinity | Not more than 0.2 ml of 0.1M hydrochloric acid or 0.1M sodium Hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator. |
| Tartrate | No crystalline precipitate is formed. |
| Heavy Metals | Not more than 0.001%. |
| Assay | 99.0 % to 100.5 % (On Anhydrous Basis) |
| Tests | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White or almost white, crystalline powder or white or almost white, granular crystals, slightly deliquescent in moist air. |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 %). |
| Identification A. Citrates B. Sodium | 1. Violet colour, turning to violet-blue is produced. 2. A white precipitate soluble in 6M acetic acid. |
| Identification B. Sodium | 1. A dense, white precipitate is formed. |
| Appearance of Solution | Solution S is clear and colourless. |
| Acidity or Alkalinity | Not more than 0.2 ml of 0.1M hydrochloric acid or 0.1M sodium Hydroxide is required to change the colour of the indicator. |
| Readily Carbonisable Substances | The solution is not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y2 or GY2. |
| Chloride | Not more than 50 ppm |
| Oxalate | Not more than 300 ppm (calculated as anhydrous oxalic acid). |
| Sulphate | Not more than 150 ppm |
| Heavy Metals | Not more than 10 ppm |
| Water | 11.0 per cent to 13.0 per cent, determined on 0.300 g. |
| Assay | 99.0 % to 101.0 % (On Anhydrous Basis) |
| Tests | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Description | White, granular crystals or white crystalline powder; odourless; Slightly deliquescent in moist air. |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in water; practically insoluble in ethanol (95%) and in ether. |
| Identification A. Citrates | 1. A dense, white precipitate is formed. 2. A yellow, crystalline precipitate is formed. |
| Identification B. Sodium | 1. A white precipitate soluble in 6M acetic acid. |
| Appearance of Solution | Solution A is clear and colourless. |
| Acidity or Alkalinity | Not more than 0.5 ml of 0.05M sulphuric acid or 0.1M sodium Hydroxide is required. |
| Arsenic | Not more than 2 ppm |
| Heavy Metals | Not more than 10 ppm |
| Chloride | Not more than 100 ppm |
| Oxalate | Not more than 300 ppm (calculated as anhydrous oxalic acid). |
| Sulphate | Not more than 150 ppm |
| Tartrate | No crystalline precipitate is formed. |
| Readily Carbonisable Substances | The solution is not more intensely coloured than reference Solution YS2 or GYS2. |
| Water | 11.0 to 13.0 per cent, determined on 0.3 g. |
| Assay | 99.0 % to 101.0 % (On Anhydrous Basis) |
| Tests | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Description | White, granular crystals or white crystalline powder; odourless; Slightly deliquescent in moist air. |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in water; practically insoluble in ethanol (95%) and in ether. |
| Identification A. Citrates | 1. A dense, white precipitate is formed. 2. A yellow, crystalline precipitate is formed. |
| Identification B. Sodium | 1. A white precipitate soluble in 6M acetic acid. |
| Appearance of Solution | Solution A is clear and colourless. |
| Acidity or Alkalinity | Not more than 0.5 ml of 0.05M sulphuric acid or 0.1M sodium Hydroxide is required. |
| Arsenic | Not more than 2 ppm |
| Heavy Metals | Not more than 10 ppm |
| Chloride | Not more than 100 ppm |
| Oxalate | Not more than 300 ppm (calculated as anhydrous oxalic acid). |
| Sulphate | Not more than 150 ppm |
| Tartrate | No crystalline precipitate is formed. |
| Readily Carbonisable Substances | The solution is not more intensely coloured than reference Solution YS2 or GYS2. |
| Water | 11.0 to 13.0 per cent, determined on 0.3 g. |
| Assay | 99.0 % to 101.0 % (On Anhydrous Basis) |
| Tests | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Description | White, granular crystals or white crystalline powder; odourless; Slightly deliquescent in moist air. |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in water; practically insoluble in ethanol (95%) and in ether. |
| Identification A. Citrates | 1. A dense, white precipitate is formed. 2. A yellow, crystalline precipitate is formed. |
| Identification B. Sodium | 1. A white precipitate soluble in 6M acetic acid. |
| Appearance of Solution | Solution A is clear and colourless. |
| Acidity or Alkalinity | Not more than 0.5 ml of 0.05M sulphuric acid or 0.1M sodium Hydroxide is required. |
| Arsenic | Not more than 2 ppm |
| Heavy Metals | Not more than 10 ppm |
| Chloride | Not more than 100 ppm |
| Oxalate | Not more than 300 ppm (calculated as anhydrous oxalic acid). |
| Sulphate | Not more than 150 ppm |
| Tartrate | No crystalline precipitate is formed. |
| Readily Carbonisable Substances | The solution is not more intensely coloured than reference Solution YS2 or GYS2. |
| Water | 11.0 to 13.0 per cent, determined on 0.3 g. |
| Assay | 99.0 % to 101.0 % (On Anhydrous Basis) |
